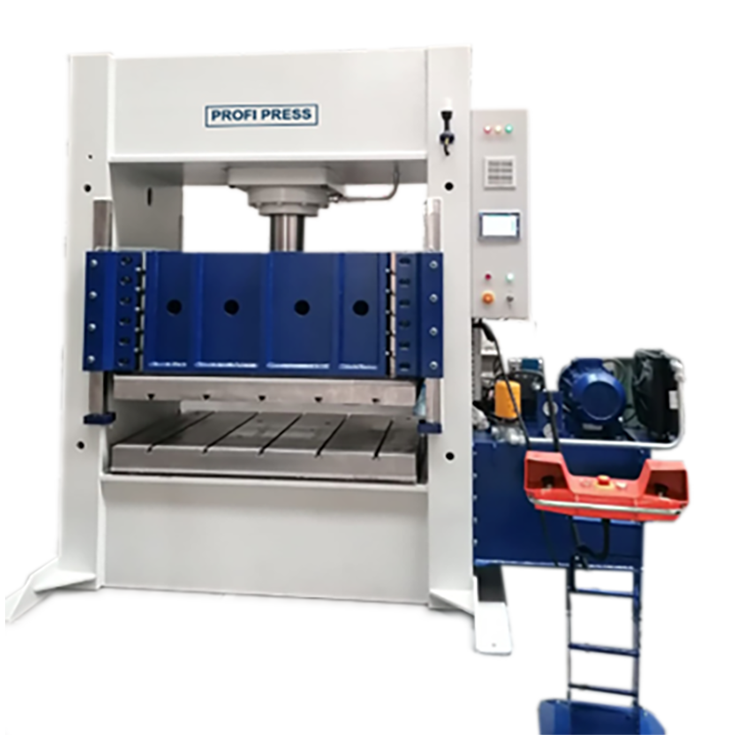
Heated Platen Presses
Some common applications for a heated platen press are for compressing composites, moulding plastics and rubber, amalgamating or vulcanising rubbers and plastics, laminating processes, forming processes, and many more.


UK Expertise
1-3 Days Delivery
USA Sales
Nationwide Service
Ireland Sales
Fast Delivery to Ireland
Worldwide
Global ShippingHydraulic Heated Platen Presses
Presses are a critical piece of machinery for a wide variety of manufacturers, and the variety and types of presses that are available on the market are limitless. There is one type of special press that allows manufacturers to not only apply pressure but also apply heat at the same time. With most standard production presses there are usually a top plate, the slide plate, and then the bolster plate which is the bottom plate but with heated platen presses the top and bottom tables are fitted with platens that are heated to a controllable temperature. What temperature can be achieved depends on how the press is designed so achievable temperature ranges vary from heated platen press to heated platen press. In addition to heating, cooling processes can also be introduced into the cycle, but once again, the availability of a cooling cycle varies from press to press.
Some common applications for a heated platen press are for compressing composites, moulding plastics and rubber, amalgamating or vulcanising rubbers and plastics, laminating processes, forming processes, and many more.
Heated Platen presses come in a variety of physical sizes, and with a variety pressing tonnages, control sets, input/outputs, safety features, loading mechanisms, table sizes, clamping systems just to name a few features that are commonly seen.
Structural Components and Materials
Metal Presses in general as well as Heated Platen Presses have a structure that is constructed with high-quality EN6 steel to create a welded unibody structure that eliminates flex and torsion within the frame during pressing operations. The longevity of a Heated Platen Press is highly reliant on the components, structural, electrical, and hydraulic, that the press is built from, so it is important to make sure the press you purchase consists of nothing but quality materials and components. A production press with heated platens built with quality components will easily withstand multitudes of production cycles over many years. Very often the platens are made from a top-quality too steel or stainless steel and can make up a substantial amount of the total weight of the press and can come in a variety of shapes and sizes and with standard DIN-650 T-Slots or customer slots for mounting tools and moulds.
Some common applications for a Heated Platen Press:
Moulding Rubber Parts and Components: Moulded Rubbers Parts and Components are created with a pressing process that forces rubbers sheets or blocks into a bespoke mould form. The shape and geometry of the mould determines what temperature the platens should be set to and what tonnage should be implemented during the pressing process.
Vulcanization: The vulcanisation process the rubber substrate is heated to temperatures that modify the overall rubber chemical structure producing components and parts with This increased elasticity and tensile strength as well as hardness.
HDPE and UHMWPE (high density and polyethylene ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene): These plastics are used for a variety of applications and both can be formed by applying intense heat and pressure creating a polymerization process that produces a material component that can accept high impact, that is chemical resistant and is easy to fabricate.
Bonding and Surface Bonding: This process is used when a smooth bond between two or more surfaces is critical and this is achieved by using an adhesive layer between two surfaces with the heated platen press melting the adhesive layer. After the adhesive is melted and the two layers are adhered together the overall bonding cycle is finished off with a controlled curing cycle which can also include a cooling cycle.
Industrial lamination: Fusing of layers can be achieved through the use of thermosetting resins. Substrates such as metal, copper, wood, plastics, paper, cotton, cloth, glass, as well as many others can be used with this process. Formation of layers whilst using the combination of high temperatures and high-pressure results in a versatile combination of electrical-mechanical and chemical properties.
Process Parameters
The manufacturing process of using a heated platen press is very often a bespoke process that has a heated platen press developed to suit that particular application, but standard heated platen presses can address many applications. There are many variables to consider when developing a heated platen press process application such as temperature control, heat distribution, curing times, required throughput for production, are a sample of the variables to be considered.
Table Size
Table sizes for all presses vary greatly and often times are manufactured to suite the customer’s requirements and tools. It is important that the customer chooses an overall bed size as well as a bed configuration including T-Slots and Mounting Slots, that results in an efficient production process. Ideally, all four sides of the press should be clear and open to facilitate automated and manual handling operations.
Heating Source
Heated platen presses can be equipped with different heating/cooling options each having their own individual advantages and disadvantages, so be sure to consult the sales technician to discuss all available options, and make sure the chosen options are suitable for your application.
Electrically Heated Platens: ideal for laminating, moulding and bonding process as well as for forming a wide variety of materials. Electrical Heated Platens provide uniform heat distribution and allow for accurate temperature control over a set period that is typically controlled by a time or an industrial HMI. Temperature ranges from 100°C to 500°C are typical but can be customised to suite the customer’s specific application and can go up to 1000°C or higher when required. As with any quality press the bolster and slide table are precision machined as it is with heated platens. Platens allow for the heating elements in the shape of cartridges or strips to be installed directly into the platen so that the transfer of heat is accurately controlled. Heat-up and cooling times can also be controlled where required and rapid heating cycles with high-wattage elements can be implemented. One other common opti8on is zoned temperature control using zone sensors to ensure proper temperatures are being reached in the appropriate zones.
Tonnages and Speeds
The required tonnage and speed required for a Heated Platen Press vary from application to application, so it is often cost-efficient to acquire a press that has a wide range of capabilities and features. Applications such as rubber molding, lamination processes, and composites forming processes have a diverse range of requirements. Required press tonnage is calculated by considering the overall projected part forming area in concert with the respective materials to be used with the pressing process. Keep in mind that excessive tonnage during pressing operations causes the use of excess energy and causes excessive tooling wear.
Heated platen presses range from 15 to 1000 tons, but once again, any tonnage is available to suit your requirements. Parameters such as speed can be configured as well as closing times and cycle times. A wide variety of industrial controllers can be used to ensure cycle time is minimized, that he forming pressure and temperatures are properly controlled, allowing the production of accurate and repeatable items while reducing costs and increasing profits.
Temperature
As well as the tonnage of the press the required platen temperature in addition to the and subsequent heat transfer to moulds for forming will be dependent on the parameters required to successfully produce a part. A proper heating and cooling system, whether it be electrical, heated oil, or steam, that is best suited for the application for both energy and cost efficiencies. Heated platen presses are used across a wide range of industries and materials, and possible temperatures can range from at or near room temperature, to 1500 °F or higher.
Cooling requirements can also be a functionality that is included in the heated platen press system facilitating curing and ensuring parts and moulds can be safely handled after production is complete and during tool change. The cooling system to be integrated into the press system depends on a variety of factors that include the geometry size of the mould part, and then the material properties of the component.
Stroke and Daylight
For any press including Heated Platen Presses, daylight refers to the maximum vertical and horizontal front opening of the press and these parameters are referred to as vertical and horizontal daylight. This is important to consider not only when you already have a variety of toolsets that need to go into a new press, but also when looking into the future the press must be able to accept dies and moulds for any products that are on the horizon.
Stroke refers to the maximum length that the piston or crank shaft can extend, and is more often than not an adjustable setting on presses of all types. The stroke is typically defined by the maximum stroke the press can attain. With modern presses the stroke is controlled with an industrial controller or computer and the parameter can often be altered with a touchscreen input. So for example if want a 100 mm stroke, you go to the HMI and then to the stroke setting, and you enter the 100 mm parameter.
In a manufacturing facility where the press will be used to produce multiple parts the stroke and daylight must accommodate the largest current and future tooling. Keep in mind that clearance is be required for die cooling systems, in die heating systems, quick-change tooling adaptations, and automatic loading and unloading systems.
Hydraulic Heated Platen Presses
Heated Platen Hydraulic Presses prove to be an extremely versatile and valuable piece of in a variety of manufacturing facilities in a variety of industries for production purposes using a controlled temperature and forming pressure. Heated Platen Presses are also commonly used for testing in laboratory environments for the purpose of impact and crush testing, and testing heat seals.
Using the appropriate integrated hydraulic system a heated platen presses produces extreme levels of pressure enabling materials to be compacted and bonded together. Depending on the application oversized slide and tables bolsters can be used to eliminate any deflection increasing the accuracy and precision of produced parts. Oversized tables can also help ensure that the slide and bolster remain parallel, but there are other mechanisms such as a Four Column Press, that has an arrangement of four columns that keep the tables perfectly parallel. Square and parallel tables is critical for forming applications and ensure reliable and repeatable processes enhancing accuracy and operational efficiencies, which for such industries as automotive and aerospace high precision is essential.
Any press that is offered can be customised and designed to accommodate a specific production process.